Understanding how the thyroid functions as well as the causes of thyroid disorders
Introduction:
The thyroid gland, located in the front of the neck, plays a vital role in regulating various bodily functions. This small, butterfly-shaped gland produces hormones that influence metabolism, growth, development, and energy levels. However, when the thyroid gland malfunctions, it can lead to a range of disorders with significant health implications. In this article, we will delve into the intricate workings of the thyroid gland, the hormones it produces, and some common disorders associated with thyroid dysfunction.
- Anatomy and Function of the Thyroid Gland The thyroid gland consists of two lobes located on either side of the windpipe, connected by a narrow strip of tissue called the isthmus. It secretes two primary hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones play a crucial role in regulating the body’s metabolism, growth, and development. The thyroid gland is controlled by the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis, a complex feedback mechanism that ensures hormonal balance.
- Thyroid Hormones: T3 and T4 Thyroxine (T4) is the main hormone secreted by the thyroid gland, accounting for approximately 90% of the total thyroid hormone production. T4 is converted into the more active triiodothyronine (T3) in various tissues throughout the body. T3 is responsible for regulating metabolism, energy production, body temperature, and the functioning of vital organs. These hormones are crucial for maintaining normal growth and development in children and regulating metabolic processes in adults.
III. Hypothyroidism: Underactive Thyroid Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland fails to produce sufficient thyroid hormones. This condition can result from various factors, including autoimmune disorders (such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis), iodine deficiency, certain medications, or damage to the thyroid gland. Common symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, sensitivity to cold, dry skin, and depression. Proper diagnosis and treatment, usually involving thyroid hormone replacement therapy, can help manage the symptoms and restore hormonal balance.
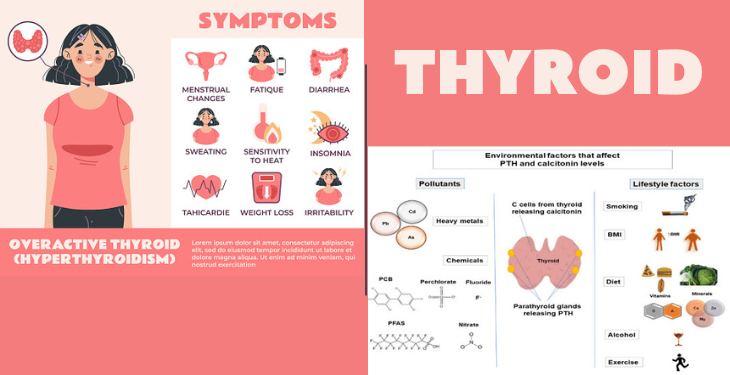
- Hyperthyroidism: Overactive Thyroid Hyperthyroidism refers to an overproduction of thyroid hormones, causing an acceleration of the body’s metabolic processes. Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder, is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. Symptoms include weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, irritability, and heat intolerance. Treatment options for hyperthyroidism include medications, radioactive iodine therapy, and, in some cases, surgery.
- Goiter: Enlarged Thyroid Gland Goiter is a condition characterized by an enlarged thyroid gland. It can occur due to iodine deficiency, thyroid nodules, or underlying thyroid disorders like hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. Goiters may cause swelling in the neck, difficulty swallowing or breathing, and a visible lump. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may involve medication, iodine supplements, or surgical removal.
VI Thyroid Cancer Thyroid cancer is relatively rare but can occur in individuals of any age. It typically manifests as a lump or nodule in the thyroid gland. Most thyroid cancers have a favorable prognosis and a high survival rate if detected and treated early. Treatment options include surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, and sometimes radiation or chemotherapy.
Conclusion:
The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Understanding its function, hormones, and common disorders is essential for early detection, diagnosis, and effective management of thyroid-related conditions. Regular check-ups, awareness of symptoms, and appropriate
Both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
- Fatigue
- Weight gain or loss
- Heat intolerance or sensitivity to cold
- Difficulty concentrating
- Heart palpitations
- Muscle weakness
- Hair loss
- Dry skin
- Irregular menstrual periods
If you have any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and treatment.
There are a number of things that can cause thyroid problems, including:
- Autoimmune diseases, such as Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- Iodine deficiency
- Thyroiditis, which is inflammation of the thyroid gland
- Thyroid cancer
Here are some tips for managing thyroid problems:
- See your doctor regularly for checkups and blood tests.
- Take your medication as prescribed.
- Eat a healthy diet and exercise regularly.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Get enough sleep.
- Manage stress.
If you have any questions or concerns about thyroid problems, talk to your doctor.
